Knee Pain
Knee pain can have many different causes, including:
- Osteoarthritis: This is a degenerative joint disease that causes the breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: This is an autoimmune disorder that can cause inflammation and damage to the knee joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Tendinitis: This is inflammation of the tendons in the knee, often caused by overuse or repetitive motion.
- Bursitis: This is inflammation of the small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint.
- Meniscus tears: The meniscus is a piece of cartilage in the knee that can tear due to sudden twisting or overuse.
- Ligament injuries: The knee has four main ligaments that can be injured, including the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the medial collateral ligament (MCL).
- Patellar tendinitis: This is inflammation of the tendon that connects the kneecap to the shinbone, often caused by overuse or repetitive motion.
- Knee fractures: Fractures of the knee can cause significant pain and swelling.
- Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint, which can cause severe pain and swelling.
The specific cause of knee pain will depend on the individual and their medical history, and it is important to seek a medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
- Experience: 15+ years in stem cell therapies
- Effective Treatments: Using your stem cells or MSCs for pain relief, regeneration, and more.
Regenerative Treatments
How does it work?
Stem cells are special cells that have the ability to develop into different types of cells in the body, such as muscle, bone, and cartilage cells. By harvesting these cells from the patient’s own bone marrow, they can be injected into the damaged area to promote healing and tissue regeneration.
During the painless procedure, a small amount of bone marrow is typically taken from the patient’s hip bone using a needle. The bone marrow is then processed to isolate the stem cells, which are then injected into the affected area using imaging guidance to ensure accurate placement.
While it may not provide immediate pain relief, it provides long-term benefits and improves overall function and quality of life. If you are considering this treatment option, it is important to book your FREE consultation with us to determine if it is right for you.
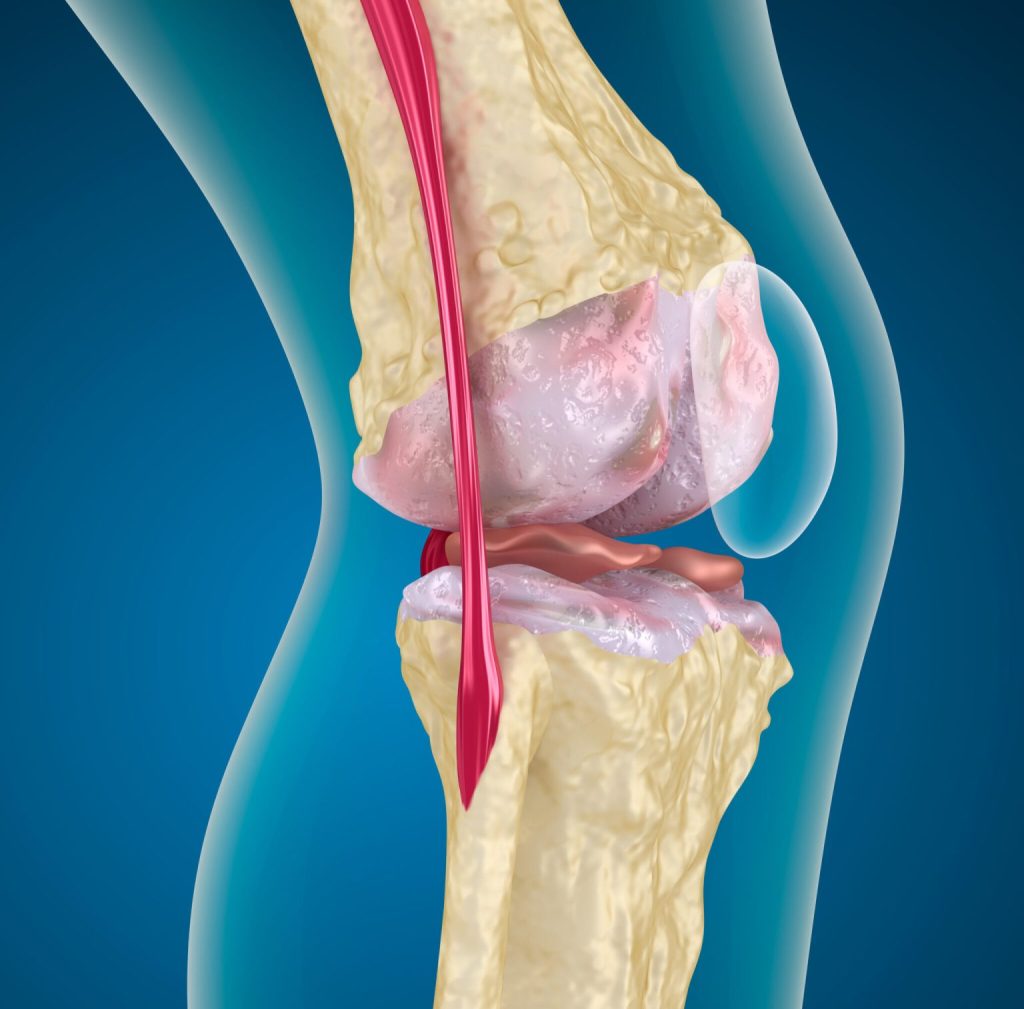
How can regenerative medicine treatments help with knee pain?
Regenerative medicine treatments can potentially help with knee pain by promoting the body’s natural healing processes and repairing damaged tissue. Some of the most common regenerative medicine treatments for knee pain include:
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: This involves using the patient’s own blood, which is processed to concentrate platelets and growth factors, and then injected into the knee joint. The platelets and growth factors stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Stem cell therapy: Stem cells are cells that have the ability to develop into different types of cells in the body. In stem cell therapy for knee pain, stem cells are typically harvested from the patient’s own bone marrow and then injected into the knee joint. The stem cells can help regenerate damaged tissue and reduce inflammation.
It’s important to note that while these regenerative medicine treatments may be effective for some patients, they may not be appropriate for everyone. It’s important to discuss the risks and benefits of these treatments with a qualified healthcare professional.
Types of Stem Cells :
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs)
Found in early-stage embryos. Super powerful, can become any cell in the body. They are not typically used in modern clinical settings in the U.S. We don’t offer treatments using ESCs.
Adult Stem Cells (ASCs)
Found in tissues like bone marrow and fat. Their job is to maintain and repair the tissue they come from. These are what we mostly use in regenerative medicine. We do offer treatments using ASCs.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
This is the type A subtype of adult stem cells found in bone marrow, fat, and umbilical cords. They're amazing at reducing inflammation, modulating the immune system, and helping damaged tissue heal. We do offer treatments using MSCs.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Regular adult cells that scientists “reprogram” to act like embryonic stem cells. Big in research, not widely used yet in clinical care. We do not work with iPSCs.
Types
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are your body’s raw materials—basically, the building blocks for all other cells. They’re special because they can:
1. Divide and make more copies of themselves (self-renew).
2. Turn into specialized cells like muscle, bone, nerve, skin, or blood cells (differentiate).
Think of them like the body’s repair system. If you get injured or sick, stem cells can go to the area and help regenerate damaged tissue.

Stem Cell Therapy
What Are Exosomes?
Exosomes are microscopic particles (about 1/1000th the size of a cell) naturally released by cells—especially stem cells. They’re loaded with growth factors, proteins, RNA, and other signaling molecules that tell other cells what to do.
Exosomes aren’t stem cells themselves. They’re what stem cells use to communicate and activate healing in your body. You could say they’re the “brains” behind the operation, coordinating the regenerative process.
We use Umbilical Cord-Derived MSC Exosomes derived from Wharton’s Jelly in donated umbilical cords. These are the most clinically used exosomes today due to their potency, safety, and ethical sourcing. They’re young, non-immunogenic, and highly active. They are excellent for orthopedic, autoimmune, and anti-aging protocols
Healing Solutions
Regenerative Therapies for Joint and Tissue Repair

Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) Therapy
What They Are: MSCs are adult stem cells derived from Wharton’s Jelly in umbilical cords. They are immune-privileged and have powerful anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties.
Applications:
- Anti-aging and aesthetic treatments
- Joint and spine degeneration
- Hair Restoration
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Autoimmune conditions
- Chronic inflammation
- Soft tissue injuries
- Neuroinflammation
Benefits:
- Potent anti-inflammatory action
- Promote tissue regeneration
- No immune rejection
- Can improve quality of life and mobility
Good Candidates:
- Patients with arthritis, chronic joint pain, neurological conditions such as autism, Alzheimer’s, and autoimmune conditions
- Those looking to avoid or delay surgery
Not Ideal For:
- Individuals with active cancer or infections
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
Pros:
- Fast, long-lasting results
- No downtime
- May delay or eliminate the need for surgery
Cons:
- Results may vary based on age and condition
- Not covered by insurance

MSC-Derived Exosomes
What They Are: Exosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles secreted by stem cells. They carry RNA, proteins, and growth factors that direct cells to heal and regenerate.
Applications:
- Anti-aging and aesthetic treatments
- Joint and spine degeneration
- Hair Restoration
- Autoimmune conditions
- Chronic inflammation
- Neuroinflammation
- Post-surgical recovery
Benefits:
- Cell-free therapy
- High concentration of signaling molecules
- Are powerful anti-inflammatories and promote tissue repair
- Work fast
- Stimulate collagen, elastin, and hair follicle regeneration
Not Ideal For:
- Individuals with active cancer or infections
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
Pros:
- No live cells (lower regulatory risk)
- No downtime
- Fast, long-lasting results
Cons:
- Results may vary based on age and condition
- Not covered by insurance

Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC)
What It Is: BMAC is a concentrate of stem cells and growth factors harvested from the patient’s own bone marrow, typically from the hip.
Applications:
- Joint regeneration
- Spinal disc repair
- Soft tissue and ligament injuries
Benefits:
- Autologous (comes from your own body)
- Rich in stem cells and regenerative factors
Good Candidates:
- Patients with mild joint damage
- Active individuals with sports injuries
Not Ideal For:
- Advanced osteoarthritis
- Order patients because of the lower bone marrow stem cell counts and their potency
Pros:
- Safe and well-tolerated
- Personalized to your biology
Cons:
- Requires harvesting procedure
- May not be effective in advanced degeneration due to the potency of the patient’s stem cells

Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
What It Is: PRP is created from your own blood. After centrifugation, the platelet-rich layer is injected into the area needing healing.
Applications:
- Tendonitis and muscle injuries
- Skin rejuvenation
Benefits:
- Natural and safe
- Accelerates tissue repair
- Minimal risk of reaction
Good Candidates:
- Early-stage injuries or hair loss
Not Ideal For:
- Severe degeneration
- Platelet dysfunction disorders
Pros:
- No downtime
- Low cost compared to other regenerative therapies
Cons:
- Results can be subtle or temporary
- Requires multiple sessions
- Not as potent compared to stem cells and exosomes therapy

Alpha-2-Macroglobulin (A2M)
What It Is: A2M is a large plasma protein that captures and neutralizes enzymes that break down cartilage in joints. A2M is isolated from your own blood.
Applications:
- Early-stage osteoarthritis
- Post-traumatic joint pain
Benefits:
- Protects cartilage from further breakdown
- Can slow progression of arthritis
Good Candidates:
- Patients with early joint degeneration
Not Ideal For:
- Advanced arthritis
- Bone-on-bone cases
Pros:
- Targeted joint protection
- Minimally invasive
Cons:
- Limited to specific joint applications
- Not regenerative on its own

Clarix Flo (Amniotic Injectable)
What It Is: Clarix Flo is an injectable made from amniotic membrane and umbilical cord tissue. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-scarring, and regenerative properties. It is FDA approved.
Applications:
- Tendon and ligament injuries
- Post-surgical recovery
- Joint pain
Benefits:
- Reduces scar formation
- Promotes soft tissue healing
- May reduce recovery time
Good Candidates:
- Active individuals with soft tissue injuries
- Post-operative patients
- Patients with history of cancer
Not Ideal For:
- Severe structural damage
Pros:
- FDA registered
- Injectable, non-invasive
- Doesn’t require to draw patient’s blood
- Can be used adjunctively with other therapies
Cons:
- Not a standalone fix for structural problems
- Higher cost than standard injections
Book Appointment
Get in Touch with Miami Stem Cell
Call Us
(305) 598-7777
Email Us
info@stemcellmia.com
Address:
7330 SW 62nd Place, Suite 320A South Miami, Florida 33143
1401 S Beretania St, Ste 400 Honolulu, HI 96814


